Are you confused about carbohydrates and their role in your diet? Do you find yourself wondering if carbs are a friend or foe? With all of the conflicting information out there, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed and unsure of what to believe. That’s why we’ve put together this complete carbohydrate guide to help you separate fact from fiction. In this article, we’ll explore the history of carbohydrates, their role in a healthy diet, and the truth about common myths and misconceptions. Whether you’re looking to lose weight, improve athletic performance, or simply lead a healthier lifestyle, this guide will provide you with the information you need to make informed decisions about your diet. So, let’s dive in and uncover the truth about carbohydrates.
What are Carbohydrates?

Carbohydrates are one of the three essential macronutrients needed by the human body to function properly. They are molecules made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. When consumed, carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which is then used by the body for energy. Carbohydrates are found in a wide variety of foods, including fruits, vegetables, grains, and dairy products. They are essential for optimal brain function, athletic performance, and maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
The History of Carbs
Carbohydrates have been the subject of much debate and controversy over the years. In the 1980s and 1990s, low-fat diets were popular, and carbohydrates were often demonized as being responsible for weight gain and other health problems. However, more recent research has shown that not all carbohydrates are created equal and that they are an important part of a healthy diet.
Low-carb diets, such as the Atkins diet, gained popularity in the early 2000s as a way to lose weight quickly. While low-carb diets can be effective for weight loss, they are not necessarily the healthiest option. Carbohydrates provide important nutrients and are essential for optimal brain function and athletic performance.
Simple vs. Complex?
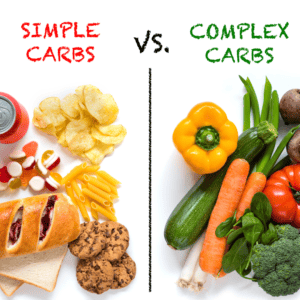
Carbohydrates can be divided into two categories: simple and complex. Simple carbohydrates are made up of one or two sugar molecules and are quickly digested by the body. They provide a quick source of energy but can cause a spike in blood sugar levels. Examples of simple carbohydrates include sugar, honey, and fruit juice.
Complex carbohydrates, on the other hand, are made up of long chains of sugar molecules and are digested more slowly by the body. They provide a sustained source of energy and are better for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. Examples of complex carbohydrates include whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
It’s important to choose complex carbohydrates over simple carbohydrates for several reasons. First, simple carbohydrates can cause a rapid rise in blood sugar levels, which can lead to a crash in energy levels and cravings for more simple carbohydrates. Second, complex carbohydrates are typically higher in fiber, which helps to regulate digestion, lower cholesterol levels, and control blood sugar levels.
Foods that are high in simple carbohydrates, such as candy and soda, are often referred to as “empty calories” because they provide little to no nutritional value. On the other hand, foods that are high in complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains and vegetables, are typically high in important nutrients such as fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
Overall, choosing complex carbohydrates over simple carbohydrates is an important part of a healthy and balanced diet. It can help to regulate blood sugar levels, improve digestion, and provide important nutrients for optimal health and wellness.
Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load

The glycemic index (GI) is a measure of how quickly a carbohydrate raises blood sugar levels. High GI foods cause a rapid rise in blood sugar levels, while low GI foods cause a slower rise. Foods with a high GI include white bread, white rice, and candy. Foods with a low GI include whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
The glycemic load (GL) takes into account both the GI and the amount of carbohydrates in a food. It provides a more accurate measure of how a food affects blood sugar levels. For example, watermelon has a high GI, but a low GL because it contains relatively few carbohydrates.
Eating foods with a high GI or GL can cause a rapid rise in blood sugar levels, which can lead to a crash in energy levels and cravings for more simple carbohydrates. This can contribute to weight gain, insulin resistance, and other health problems.
Choosing foods with a low GI and GL can help to regulate blood sugar levels, improve energy levels, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are all good choices for low GI and GL foods. Incorporating fiber-rich carbohydrates into your diet can also help to improve blood sugar control and overall health.
It’s important to note that the GI and GL are just two factors to consider when choosing carbohydrates for your diet. It’s also important to consider the overall nutritional value of the food and to balance carbohydrates with protein and healthy fats. By choosing the right carbohydrates and balancing your diet, you can improve overall health and wellness.
Fiber

Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that the body cannot digest. Unlike other carbohydrates, fiber passes through the digestive system largely intact. Fiber is found in a variety of foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
Fiber provides many health benefits. First and foremost, fiber helps to regulate digestion. It adds bulk to the stool, making it easier to pass, and can help to prevent constipation. Fiber can also help to lower cholesterol levels, which can reduce the risk of heart disease. Additionally, fiber can help to control blood sugar levels by slowing down the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream.
There are two types of fiber: soluble and insoluble. Soluble fiber dissolves in water and forms a gel-like substance in the digestive tract. This type of fiber can help to lower cholesterol levels and control blood sugar levels. Insoluble fiber does not dissolve in water and adds bulk to the stool, helping to promote regular bowel movements.
Fiber is an essential part of a healthy and balanced diet. Unfortunately, many people do not consume enough fiber in their diets. The recommended daily intake of fiber is 25 grams for women and 38 grams for men. Incorporating fiber-rich carbohydrates into your diet can help to improve overall health and wellness.
Good sources of fiber include fruits such as apples, pears, and berries, vegetables such as broccoli, carrots, and spinach, whole grains such as oatmeal, brown rice, and whole wheat bread, and legumes such as beans and lentils. By choosing fiber-rich carbohydrates and incorporating them into your diet, you can enjoy the many health benefits of fiber.
The Truth About Carbohydrates: Myths vs. Facts
Carbohydrates have been the subject of much debate and controversy over the years. From fad diets to conflicting research, it can be difficult to separate fact from fiction when it comes to carbohydrates. In this section, we will take a closer look at some of the most common myths and facts about carbohydrates. By understanding the truth about carbohydrates, you can make informed decisions about your dietary choices and optimize your health and wellness.
Myth #1: Carbs make you gain weight
Carbohydrates do not cause weight gain in and of themselves. Consuming too many calories, regardless of the source, can lead to weight gain.
Myth #2: All carbs are created equal
Not all carbohydrates are created equal. Simple carbohydrates can cause a rapid rise in blood sugar levels, while complex carbohydrates provide a more sustained source of energy.
Myth #3: Low-carb diets are the healthiest option
Low-carb diets can be effective for weight loss, but they are not necessarily the healthiest option. Carbohydrates provide important nutrients and are essential for optimal brain function and athletic performance.
Fact #1: Carbs are essential for energy and brain function
Carbohydrates provide the body with the energy it needs to function properly and are essential for optimal brain function.
Fact #2: Complex carbs can actually aid in weight loss
Complex carbohydrates provide a sustained source of energy and can help to keep you feeling full and satisfied. This can lead to a decrease in overall calorie intake and aid in weight loss.
Fact #3: Low-carb diets can have negative health consequences
Low-carb diets can lead to a decrease in overall nutrient intake and can cause negative health consequences.
The Science of Carbohydrates
Understanding the science behind how carbohydrates are metabolized by the body, the relationship between carbohydrates and insulin, and the impact of carbohydrates on athletic performance and gut health can help to inform dietary choices and improve overall health. In this section, we will explore the science of carbohydrates and its importance for a healthy lifestyle.
Metabolism

Metabolism is the process by which the body converts food into energy. Carbohydrates play a crucial role in this process, as they are the primary source of fuel for the body. When carbohydrates are consumed, they are broken down into glucose, which is then used by the body for energy. The body’s metabolism converts glucose into ATP, which is the molecule that provides energy for all of the body’s cellular processes.
Metabolism is a complex process that is influenced by a variety of factors, including age, gender, body composition, and activity level. A person’s basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the amount of energy that the body uses at rest. BMR is influenced by factors such as age, gender, and body composition. As a person ages, their BMR typically decreases, which can lead to weight gain and other health problems.
The body’s metabolism can also be influenced by factors such as diet and exercise. Consuming a diet that is high in complex carbohydrates and low in simple carbohydrates can help to regulate blood sugar levels and improve overall metabolism. Regular exercise can also help to boost metabolism and improve overall health and wellness. By making healthy lifestyle choices and understanding the role of carbohydrates in metabolism, you can optimize your body’s energy production and improve overall health and wellness.
Insulin
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels. When carbohydrates are consumed, they are broken down into glucose, which is then transported through the bloodstream to cells throughout the body. In response to rising blood sugar levels, the pancreas releases insulin, which signals cells to take up glucose from the bloodstream.
Insulin is particularly important for people with diabetes, a condition in which the body is unable to produce or use insulin effectively. In people with type 1 diabetes, the pancreas produces little or no insulin, while in people with type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to insulin, making it less effective at regulating blood sugar levels.
For people with diabetes, managing carbohydrate intake is crucial for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. Carbohydrates have the greatest impact on blood sugar levels, and consuming too many carbohydrates at once can cause a rapid rise in blood sugar levels, which can be dangerous for people with diabetes.
However, it’s important to note that not all carbohydrates are created equal. Complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, are digested more slowly by the body and have a smaller impact on blood sugar levels than simple carbohydrates, such as candy and soda. By choosing the right types and amounts of carbohydrates and balancing them with protein and healthy fats, people with diabetes can maintain healthy blood sugar levels and improve overall health and wellness.
Gut Health
Gut health is a key component of overall health and wellbeing, and carbohydrates play an important role in maintaining a healthy gut. Fiber-rich carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes, are particularly important for promoting gut health. Fiber is not digested by the body and instead passes through the digestive system largely intact. This helps to regulate digestion, promote the growth of healthy gut bacteria, and reduce the risk of certain gut-related diseases, such as colon cancer and inflammatory bowel disease. Eating a diet rich in fiber can also help to reduce inflammation in the gut, which is linked to a number of chronic diseases, including heart disease and diabetes. By incorporating fiber-rich carbohydrates into your diet, you can promote overall gut health and improve your overall health and wellbeing.
Heart Health

There has been much debate over the years about the relationship between carbohydrates and heart health. Some studies have suggested that a diet high in carbohydrates, particularly refined carbohydrates, may increase the risk of heart disease. However, other studies have shown that a diet rich in complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, can actually reduce the risk of heart disease.
One possible explanation for these conflicting results is that not all carbohydrates are created equal. Simple carbohydrates, such as sugar and white flour, can cause a rapid rise in blood sugar levels and may contribute to inflammation and oxidative stress, which are risk factors for heart disease. Complex carbohydrates, on the other hand, are digested more slowly by the body and are less likely to cause spikes in blood sugar levels.
Additionally, many foods that are high in complex carbohydrates, such as fruits and vegetables, are also rich in other heart-healthy nutrients, such as fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Eating a diet rich in these types of carbohydrates can help to reduce the risk of heart disease and improve overall heart health.
Overall, the relationship between carbohydrates and heart health is complex and requires further research. However, it’s clear that choosing the right types of carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, can play an important role in maintaining a healthy heart.
Diabetes

Carbohydrates play a crucial role in managing diabetes. People with diabetes need to carefully manage their blood sugar levels to avoid complications such as heart disease, nerve damage, and kidney disease. Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which can cause blood sugar levels to rise. Therefore, it’s important for people with diabetes to monitor their carbohydrate intake and choose carbohydrates with a low glycemic index and glycemic load.
Fiber-rich carbohydrates, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, are particularly important for people with diabetes. Fiber helps to regulate digestion, lower cholesterol levels, and control blood sugar levels. Consuming fiber-rich carbohydrates can help to prevent blood sugar spikes and promote overall health and wellness.
It’s also important to balance carbohydrates with protein and healthy fats. Protein and healthy fats can help to slow down the digestion of carbohydrates and prevent blood sugar spikes. People with diabetes should work with a healthcare professional to develop a meal plan that takes into account their individual needs and preferences.
Overall, carbohydrates are an important part of a healthy and balanced diet for people with diabetes. By choosing the right types and amounts of carbohydrates and balancing them with protein and healthy fats, people with diabetes can optimize blood sugar control and improve overall health and wellness.
Carbohydrates in Your Diet

Carbohydrates are an essential part of a healthy and balanced diet. When choosing carbohydrates for your diet, it’s important to focus on complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. These types of carbohydrates provide important nutrients and are better for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
It’s also important to balance carbohydrates with protein and healthy fats. Protein and healthy fats can help to keep you feeling full and satisfied, and can also provide important nutrients for overall health and wellness.
When calculating your daily carbohydrate needs, it’s important to consider your individual needs based on factors such as age, gender, activity level, and overall health status. A registered dietitian can help to determine your individual carbohydrate needs and provide personalized recommendations for your diet.
Overall, carbohydrates are an important part of a healthy and balanced diet. By choosing the right types and amounts of carbohydrates and balancing them with protein and healthy fats, you can optimize overall health and wellness.
Carbohydrate Diets

Low-carbohydrate diets, such as the Atkins diet and the ketogenic diet, have gained popularity in recent years as a way to lose weight and improve health. These diets typically limit carbohydrates and focus on consuming protein and healthy fats.
While low-carbohydrate diets can be effective for weight loss, they are not necessarily the healthiest option. Carbohydrates provide important nutrients and are essential for optimal brain function and athletic performance. Eliminating or severely restricting carbohydrates can lead to nutrient deficiencies, low energy levels, and other health problems.
It’s important to understand the potential risks and benefits of low-carbohydrate diets and to choose the right types and amounts of carbohydrates for your diet. Choosing complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, and balancing them with protein and healthy fats can help to improve overall health and wellness.
In summary, low-carbohydrate diets can be effective for weight loss, but they are not necessarily the healthiest option. It’s important to understand the potential risks and benefits of these diets and to choose the right types and amounts of carbohydrates for your diet to optimize health and wellness.
Carbohydrates Conclusion
Carbohydrates are an essential part of a healthy and balanced diet. Despite their reputation as “bad” or “unhealthy,” carbohydrates provide the body with the energy it needs to function properly and are essential for optimal brain function and athletic performance. Understanding the myths and facts about carbohydrates is key to making informed decisions about what to eat. By incorporating carbohydrates into your diet in a healthy and balanced way, you can improve overall health and wellness. Remember to choose complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, and balance them with protein and healthy fats. By following the tips and guidelines outlined in this guide, you can enjoy the benefits of carbohydrates while maintaining a healthy and balanced diet.

